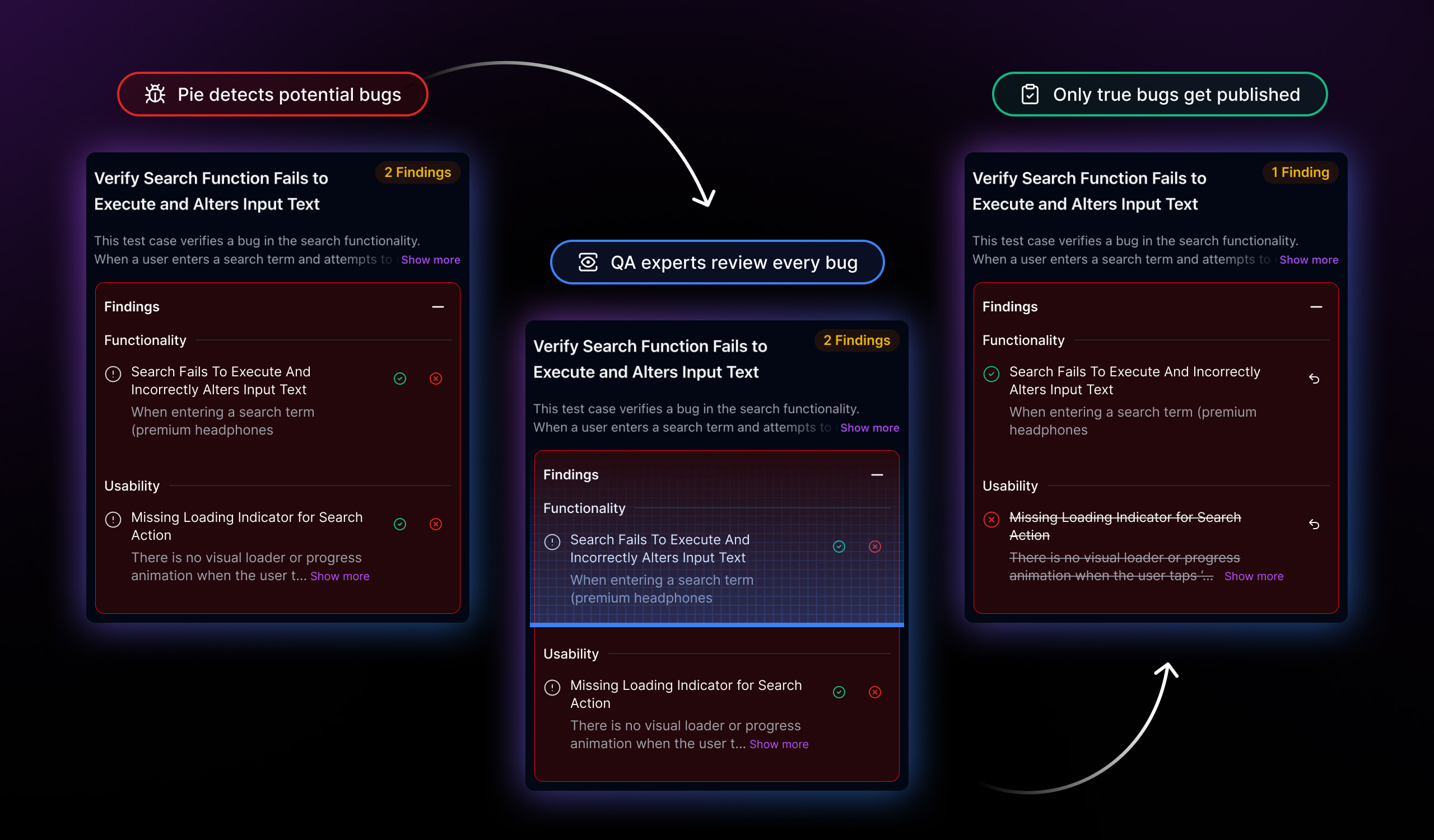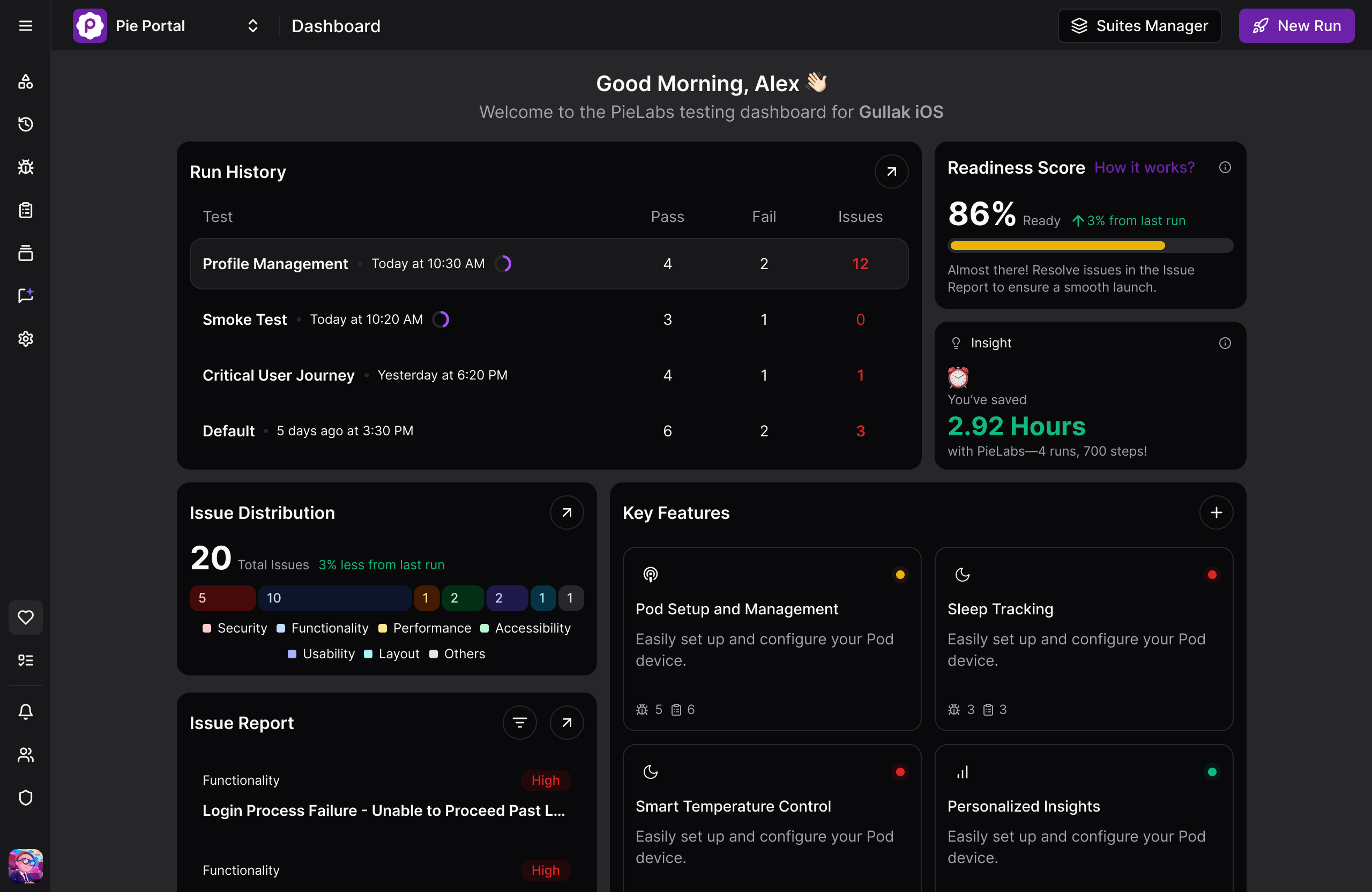
10,000 hours of QA
In 30 Minutes
The world's fastest QA platform. Deploy AI agents that think and test like your actual users. 80% E2E coverage in 30 minutes. Whether your code comes from humans or AI, Pie tests it all.
Web • iOS • Android